Northeast Commodity Values Decline in Q2 2025
Northeast Recycling Council (NERC) Publishes 25th Report Marking Six Years of Quarterly Data
NERC’s Material Recovery Facilities (MRF) Commodity Values Survey Report for the period April - June 2025 showed a decline in the average commodity prices for Q2 2025. The average value of all commodities decreased by 5.99% without residuals to $96.21 and by 7.74% with residuals to $82.68, as compared to last quarter. Single stream decreased by 5.70% without residuals and 8.30% with residuals, while dual stream / source separated decreased by 7.00% without residuals and 7.16% with residuals compared to last quarter. Dual stream MRFs saw a slightly smaller decrease with residuals than single stream.
Individual commodity price averages this quarter denote the decrease felt across all commodity categories apart from glass and the special cases of mixed paper, aseptic and gable-top cartons, and mixed plastic.
Average Blended Commodity Value Per Ton: Q2 2019 – Q2 2025
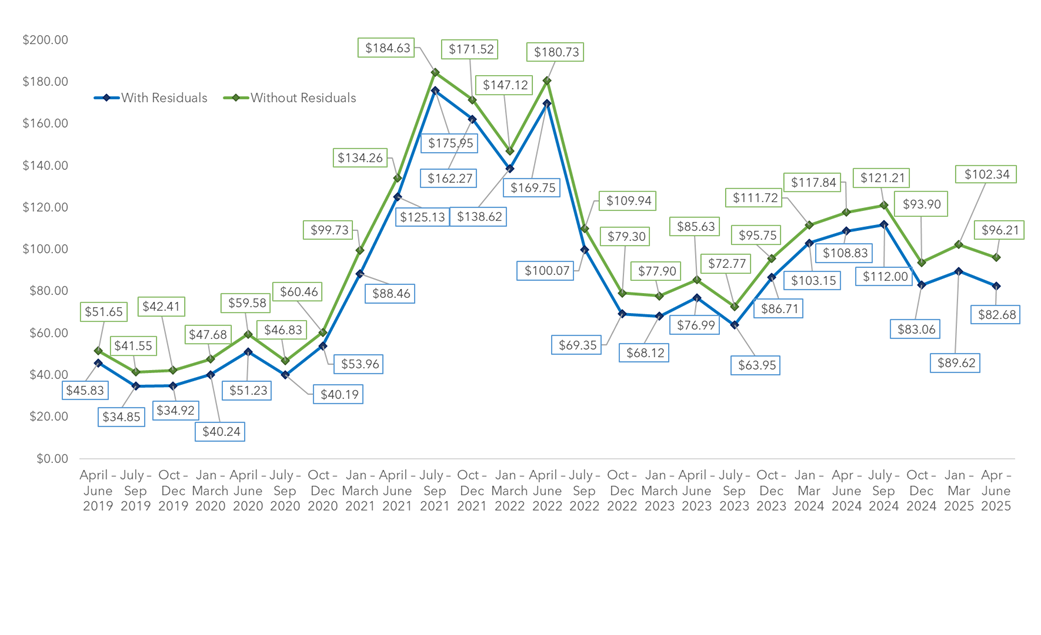
This is the 25th quarterly report in NERC’s series of reports on the market value of commodities from MRFs in the Northeast. This report includes information from 19 MRFs representing twelve (12) states: Connecticut, Delaware, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, and Virginia.
These survey results reflect the differing laws and collection options in the participating states. Five of the states included in this report have beverage container deposit laws. As a result, fewer glass bottles, PET bottles and aluminum cans are processed in MRFs in those states. Those MRFs are also likely to have less revenue from those recyclables. In addition, the report reflects a mix of single stream, dual stream, and source separation to collect recyclables with single stream being the most common approach. The type of collection used will have an impact on MRF design and operation. Thus, the data from this report reflects the unique blend of facilities and statewide laws in the reporting states.
Residual refers to the incoming material that cannot be marketed and goes to disposal. The value without residuals reflects the value of a perfect ton of marketed material, while the value with residuals reflects the value of each ton processed with the costs associated of disposing unmarketable material. Note: In many cases, recovered glass goes to market but at a negative value.
This data is not intended to be used as a price guide for MRF contracts. NERC’s database represents single and dual stream MRFs, states with and without beverage container deposits, a wide variety in markets and geographic access to markets, and variety of materials collected for processing at the participating facilities. As a result, it represents the diversity of operating conditions in these locations and should not be used as a price guideline for a specific program.
For more information, contact Megan Schulz-Fontes, Executive Director, at megan@nerc.org.
Share Post





