NERC News:
All Posts

Established in 2015, Apparel Impact has been working within their community to reduce textile waste, fight clothing insecurity, create jobs, and ensure those in the community in need of clothing never go without. This family and veteran owned company is built on the foundation of disruption for good. The Apparel Impact team has been working to make real changes in an industry that has remained the same for many decades. They continuously push for transparency, accountability, and working solutions in the field. Today Apparel Impact works with over 1,800 partners and locations, including schools, towns, nonprofits, national brands, and small businesses across six states. Apparel Impact is also working to bring textile sorting and grading capacity back to the Northeast, while launching upcycling brands aimed at scaling textile reuse across the region. For Apparel Impact, it is all about “changing the way people think about clothing, proving a for-profit company can still put people and communities first, and making sure what we collect helps someone’s life, not a landfill.” Their impact and reach continue to grow every year. “Textile recovery only works at scale. It takes leadership, accountability, and real collaboration across states and sectors. We joined NERC because we believe in building infrastructure that actually changes outcomes, not just talking about it. We’re proud to stand with the NERC and others in the Northeast who are ready to move the industry forward.” NERC is excited to welcome Apparel Impact to our growing group of textile focused members. We look forward to amplifying their voice and helping to expand textile recovery in any way we can. For more information on Apparel Impact visit.

For more than a decade, Sensoneo has been driving innovation across the waste and recycling industry worldwide. Headquartered in Europe and active in more than 80 countries, the company has recently expanded into the United States by opening its Boston office. From the outset, its mission has been clear: to help cities, businesses, and governments address two of the sector’s most pressing challenges—operational efficiency and data transparency. Sensoneo brings proven, large-scale experience, operating nationwide end-to-end IT platforms for deposit return systems (bottle bill programs) in nine countries and supporting Extended Producer Responsibility programs with robust data management, reporting, and compliance tools. Its smart waste solutions power the world’s largest deployment of sensor-based waste-monitoring technology, enabling municipalities and facilities to optimize collection operations. “With the launch of our U.S. subsidiary, we are excited to expand collaboration with organizations advancing sustainable materials management and stronger recycling systems,” said Martin Nestepny, CEO of Sensoneo USA. “As a global technology partner, Sensoneo supports PROs, recyclers, and policymakers with actionable data to enhance program performance, ensure regulatory compliance, and deliver measurable environmental outcomes - priorities that closely align with NERC’s mission.” NERC is pleased to welcome Sensoneo to its growing membership and looks forward to supporting the company’s work to improve performance and drive greater effectiveness across the waste and recycling industry. For more information on Sensoneo visit.

Planet Aid is a nonprofit established in 1997 to divert clothes and shoes from the U.S. waste stream and fundraise for community development programs around the world. With thousands of donation bins and centers across the Northeast, Mid-Atlantic and Midwest, Planet Aid’s mission is to inspire positive change by making it easy for donors, partners and communities to take small steps that add up to a big impact. Over three decades, Planet Aid has collected more than two billion pounds of clothes and shoes for reuse. These donations have helped Planet Aid raise more than $100 million to fund community-led projects in the U.S., Africa, Asia, and Latin America. With headquarters just outside Baltimore, MD, Planet Aid serves thousands of communities in 14 states, including New York, New Jersey, Maine, Massachusetts, Connecticut and more. For those without a yellow collection bin or white donation center nearby, they've developed a donation through mail option. By partnering with Give Back Box, you can pack up and mail your donation items directly to their thrift store. This inclusive approach allows them to reach more communities, diverting even more waste that may have gone to a landfill or incinerator. “Planet Aid is excited to join NERC, an organization that shares our goals of minimizing waste, conserving natural resources, and advancing a sustainable economy,” said Uli Stosch, Planet Aid’s Chief Officer of Strategic Development. “We looking forward to collaborating with NERC’s members to help U.S. communities in the Northeast minimize textile waste while maximizing reuse to limit the negative impacts of fast fashion.” NERC is excited to welcome Planet Aid into our growing group of nonprofit members. We look forward to helping share the excellent work they are doing in the NE and around the world. For more information on Planet Aid visit.
Posts Sorted by Categories
In The News

MRFs in the Northeast United States reported a decrease in average prices for nearly all recycled commodities — with glass and bulky rigids providing the rare bright spot — during the third quarter of 2025, according to a report from the Northeast Recycling Council. This continues the downward trend reported in the region since Q2. In Q3, average blended commodity value without residuals was $75.14, a decrease of 21.9% from the previous quarter. When calculating the value with residuals, prices were $60.16, a decrease of 27.24%, says the quarterly MRF Commodity Values Survey Report. Single-stream MRFs saw values decrease sequentially by 23.32% without residuals and 28.86% with residuals. Dual-stream or source-separated MRFs saw decreases of 17.33% without residuals and 21.76% with residuals compared to last quarter. The report includes information from 19 MRFs representing 12 states: Connecticut, Delaware, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, and Virginia. The NERC report is meant to offer a regional look at price trends and is a part of the group’s ongoing work to promote and boost recycled commodity supply and demand in the Northeast. It surveys a variety of MRFs in numerous markets, including those in five states with beverage container deposit laws, which it says affect material flows into MRFs. NERC says its reports are not meant to be used as a price guide for MRF contracts because it “represents the diversity of operating conditions in these locations.” NERC adopted a new report format at the beginning of 2025 that now provides average prices for specific commodities in addition to aggregate values. According to the Q3 report, most commodity categories fell significantly, with the exception of glass and the “special case of bulky rigids.” The average price for bulky rigids in the quarter was $43.26, a 93% increase from the previous quarter. NERC did not offer insight into the increase. The average price for PET was $125.58 in the quarter, down 60%, while prices for Natural HDPE fetched about $955.31 a ton, down 46%. OCC saw an average price of about $86.23, down 10%, according to the report. Major publicly-traded waste companies echoed similar commodity trends during their Q3 earnings calls . Casella, which operates in the Northeast and mid-Atlantic, reported that its average recycled commodity revenue per ton was down 29% year over year in Q3. To reduce the impact from low commodity values, the company typically shares risk with customers by adjusting tip fees in down markets. Recent upgrades at a Connecticut MRF helped raise revenue for processing volumes in the quarter, executives said. Meanwhile, Republic Services is planning to build a polymer center for processing recycled plastic in Allentown, Pennsylvania, next year. During the Q3 earnings call in October, executives said they expect strong demand at such centers from both a pricing and volume standpoint, despite the decline in commodity prices. The company already has similar polymer centers in Indianapolis and Las Vegas, which consume curbside-collected plastics from Republic’s recycling centers and produce products such as clear, hot-wash PET flake and sorted bales of other plastics. Read on Waste Dive.
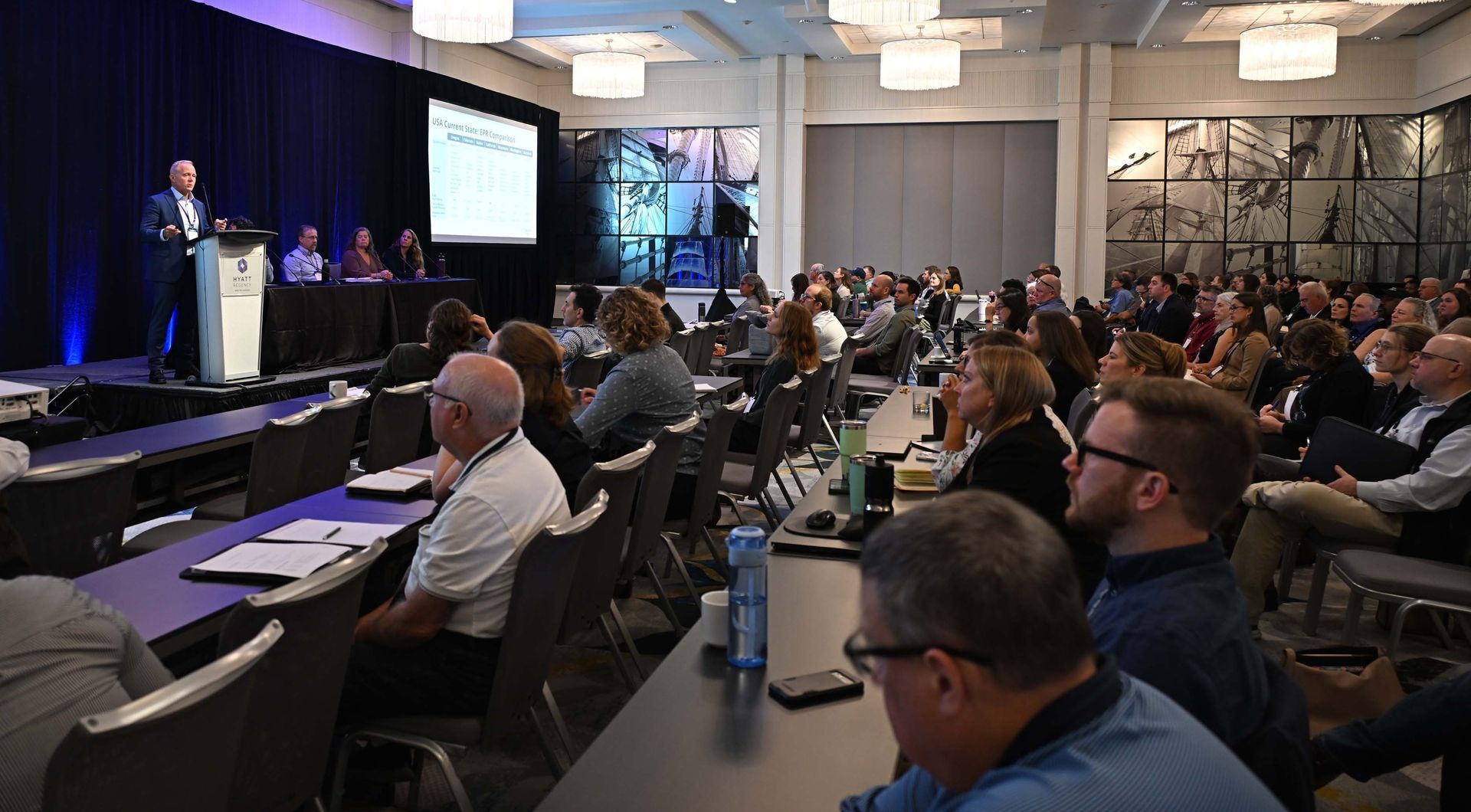

The Northeast Recycling Council (NERC) held their annual event from October 7 – 8 in Boston, MA. Renamed the Rethink Resource Use Conference, the name reflects an update in the approach of managing materials and discussing key strategies to drive sustainable practices forward in communities. “The new name, Rethink Resource Use, makes us consider how we can leave a more positive impact. NERC brings together professionals from across the materials management chain to improve management practices and ensure the health of the people and the environment. The event aims to mobilize others to take action and engage people in recycling programs, community engagement, trends, and more,” said NERC’s Executive Director, Megan Schulz-Fontes. Gathering together leaders from academia, government, and the sustainable materials industry, the conference was a great way to reconnect through networking and learning opportunities. RRU DAY ONE Material Shifts and New Terrain On Tuesday morning, October 7, Schulz-Fontes welcomed attendees to Boston and expressed that she was looking forward to having meaningful discussions and making connections with people around the industry. With great speakers from across the world, a wide range of important topics would be covered from innovations in infrastructure to technology. She also thanked talented colleagues who evaluated this event and made it even better, welcomed emerging professionals, and emphasized that it is important to acknowledge that human practices are shifting and evolving, and new programs and regulations are coming online to address the growing waste problem. We need to safeguard public health and biodiversity to help life on earth. Schulz-Fontes then introduced John Fischer, Deputy Division Director for Solid Waste Materials Management for the Massachusetts’ Department of Environmental Protection, who made the opening remarks, reflecting on Massachusetts’ Solid Waste master plan. He pointed out that they set an aggressive reduction goal—to reduce 1.7 tons of waste by 2030. While they have seen progress in certain areas, waste has continued to rise. So, they are reviewing it now to see how they can shift elements for greater progress. Massachusetts has been successful in food waste reduction (from small businesses and residents) with a waste disposal ban and recycling market grants, as well as loans to try to build the infrastructure. He said they have also seen success in their mattress disposal ban and an increase in textile recovery since implementation in 2022. There is also a long-standing disposal ban on construction waste to ensure more effective separation. In 2020, diversion was at 15% and increased to 20% in 2025. They would like to get to 30% by 2030. Fischer also pointed out that the Massachusetts DEP needs to take a comprehensive approach and grow market funding. They have collaborated with state and local health officials to create best practices with food containers and replace single waste food service ware to reusables. There are growing suites of market recycling program grants, including market reduction innovation grants launched this year. Smaller and more flexible grants could grow waste diversion over time and help facilities grow at scale. He said that while they are looking at doing the best they can to manage waste, the goal is to learn from colleagues in other states and in the business communities. David Allaway, Senior Policy Analyst, from the Oregon Department of Environmental Quality, gave the keynote address, first pointing out that about 20 years ago, they started taking a deeper look at their solid waste and recycling program and the connection with the waste and climate situation. Because of that, it caused a shift in programming. Going back to 2004, the Department was tasked with looking at solid waste management opportunities—recycling and waste prevention was primarily reducing in other states but not Oregon. The community was ready for climate protection, but emissions reductions don’t count. That was the beginning of Oregon’s Consumption-Based Greenhouse Gas Emissions Inventory (CBEI) and the results were an eye opener and the inventory has been updated since to look at current trends. The key takeaways from this was that all studies point in the same direction—materials matter! The production and use of materials does have a profound impact on our environment. Most impacts occur upstream of use and disposal. Recycling and composting can be helpful but alone are insufficient. From this, Oregon’s 2050 Vision and Framework for Action was born. This also included end of life materials. Allaway explained that the legislative report and technical supports were published last fall. For Oregon: Materials are driving growth in emissions Most emissions occur pre-purchase (most in food and vehicles and parts) Sector based emissions have flattened while consumption-based emissions have grown Emissions are out of state but not out of reach Oregon Comprehensive Climate Action Plan (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, and Solid Waste Management) includes: Landfill methane reductions Recycling improvements Expand composting Prevent wasting of food Plant-rich diets Upstream packaging EPR Reduce embodies carbon He pointed out that not all materials are equally beneficial to recycling, and not all recycling pathways are equally beneficial. Maximizing recycling is not the same as optimizing recycling. Lifecycle impacts versus material attributes begs the question; how well do popular material attributes correlate with reduced environmental impacts? When comparing different packages based on recyclability, recyclable packages are better for the environment, however, downstream impacts must be taken into consideration. Recycling and composting are a means to an end—the conservation of resources and reduction of pollution, however, not all are effective. Design your programs to maximize them instead of just chasing tonnage diversion targets. Is education effective? It depends on how recycling is communicated and how local authorities think about it and treat it. Whether it is advanced through policy through broader benefits, it depends on you and what choices you make and the paths take in the coming years. Discussions on EPR After the welcome remarks and morning keynote, focus turned to “EPR for Packaging State of Mind: Lessons and Progress in the Northeast” Moderated by Kevin Budris, Deputy Director for Just Zero, the discussion featured Jason Bergquist, Vice President of U.S. Operations for RecycleMe; Erin Victor, PhD, Member of the Senator George J Mitchell Center Research Team at the University of Maine; Shannon McDonald, Natural Resource Planner at the Maryland Department of the Environment; and David Allaway, Senior Policy Analyst for Oregon Department of Environmental Quality. Bergquist kicked it off by talking about the current EPR landscape in the U.S. Seven EPR packaging bills have been passed and 10 states have introduced legislation for EPR for packaging from 2024 to 2025; this number continues to rise. Those that have been signed into law include Oregon and Maine (2021), Colorado and California (2022), Minnesota (2024), and Washington and Maryland (2025), with implementation ranging from July 2025 to July 2029. California has the most ambitious goals—by 2032 100% of all packaging must be recyclable or compostable, 65% of all single-use plastic packaging to be recycled, and there should be a 25% reduction in packaging. He said that challenges producers face in the west are when is a producer a producer, when is a package a package, where should the focus be (fees, targets, modulation plans). There are always different definitions, two different scopes, bottle bill vs non-bottle bill, primary, secondary, tertiary—which is in scope? Victor covered the research she’s been doing the past couple of years. Her research approach included a qualitative case study of the emergence of Maine’s EPR for packaging legislation situated within a larger 24-month ethnographic research project on the politics of disposable packaging. Maine is a primarily rural state and much of it relies on drop off centers. However, the state has yet to meet the 50% waste diversion goal, so something more needs to be done. She did explain that there have been disruptions to Maine’s materials management system that have been a challenge: centralized waste planning agencies disbanded, Green Fence/National Sword, COVID, and the shuttering of the Coastal Resource of Maine facility in Hampden. Maine’s packaging journey started in 2019 when the DEP recommended EPR for packaging. In 2021, the state passed the first in the nation EPR law, the rules were adopted in 2024, and in 2025, the goal is to define ‘readily recyclable’ and selecting a stewardship organization. She emphasized that it is critical to have a strong commitment to stakeholder outreach, maintain municipal operational control over materials management, look at the need for more transparent and robust data and the burden of reporting (for both producers and municipalities), and consider what elements of packaging regulation to address through market-based approaches versus command-and-control regulations. Fortunately, LD1423 was introduced this year which really updated and harmonized the program. She said that she is currently working on estimating the impact of tradeoffs in U.S. EPR rulemaking scenarios. Read the full article on Waste Advantage.
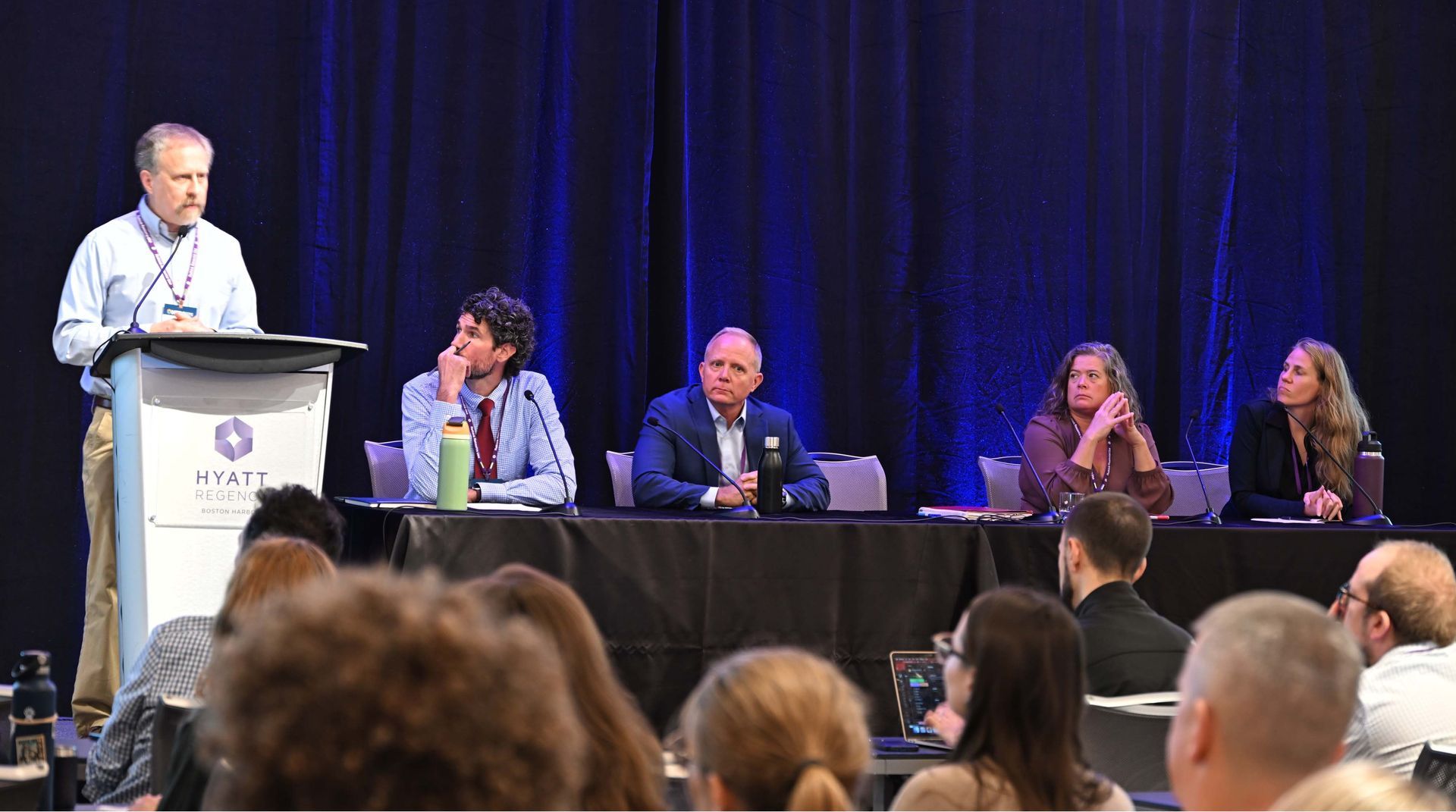

Stress levels are high for CPG companies and packaging groups as extended producer responsibility programs unfold in multiple states. This was on display at three recent Boston events hosted by the Sustainable Packaging Coalition, How2Recycle and the Northeast Recycling Council, with questions flying about costs, policy harmonization and relationships with regulators. Paul Nowak, executive director of GreenBlue, adopted the role of support group leader for a room full of representatives from many of the world’s largest CPG companies in his opening talk at SPC Advance. He reminded them that “you are not alone” and urged them to take the long view on this major industry shift. “What you see at the end of the change is not what you see during the change,” said Nowak, drawing on examples from prior industry shifts as well as other major life events. “You are in this uncomfortable period right now where it’s not moving as rapidly as you would think and you don’t have the historic perspective yet of where it could go.” Sticker shock While CPGs are familiar with EPR costs from programs in other countries, the complexity and scale of the U.S. rollout in seven states is presenting its own unique challenges. Oregon is the only state that’s begun collecting fees, and already the costs are high. Circular Action Alliance, the producer responsibility organization selected for the majority of state programs to date, estimates a budget of $188 million in the program’s first year, with that figure growing in the years ahead. Charlie Schwarze, board chair for CAA and senior director of packaging stewardship at Keurig Dr Pepper, said the costs are starting to resonate with major companies. KDP, for example, has been working to sort out different aspects of its packaging in terms of licensing arrangements, private label manufacturing partnerships and other factors. This requires a close relationship with the company’s finance, R&D and procurement teams to gather data and make cost projections. “It’s been a bit of a slow-moving process because the dollars, at least in 2025, are not extremely notable. But they’re going to get bigger pretty quickly,” he said, citing Colorado and California’s programs on the horizon. Shane Buckingham, chief of staff at CAA, said it will be months until companies have a better sense of the true costs. The group set initial fees for California, which won’t be invoiced until August 2026, but those fee levels are expected to change once SB 54 regulations are finalized . “Please don’t take our early fee schedule of being indicative of what your cost will be in 2027, it’s just a drop in the bucket,” he said. “The fees are going to go up significantly in California because we have to fund a $500 million [plastic] mitigation fund, we’re going to have system funding to improve recycling, source reduction, reuse, refill.” SPC Director Olga Kachook encouraged attendees to think about these fees as motivation to innovate rather than a burden. In her view, avoided fees through ecomodulation could be viewed as “possible new investment capital” for covering the costs of material switches, R&D, MRF testing, consumer education campaigns and more. “We can innovate to those lower fees by switching to incentivized materials and formats and then we can reinvest the savings back into sustainable materials and infrastructure that seemed out of reach,” she said. Searching for harmony All three events also featured ample discussion about if or how aspects of current EPR programs could be better aligned. While regulators are working to align certain definitions where possible, they also noted that certain state programs were uniquely designed for a reason. David Allaway, senior policy analyst at the Oregon Department of Environmental Quality, said during NERC’s Rethink Resource Use Conference that he sees a potential benefit to harmonizing ecomodulation approaches in some cases. But at the same time, he said, “I fear that the push for harmonization will lead to a race to the bottom” by potentially limiting the ability for states to craft policies based on their respective needs. As for those who critique other unique aspects of Oregon’s law, such as responsible end market requirements , Allaway said “that’s not negotiable for us,” as market issues were a leading motivation for the law in the first place. Allaway said Oregon’s system was established based on specific regional priorities, such as putting an end to exporting certain types of material that led to dumping in other countries. The state’s approach to ecomodulation and life cycle analysis is also informed by years of work on greenhouse gas inventories and consumption-based accounting, which challenges many commonly held assumptions about recyclability . Each state has its own unique factors in terms of collection access and market infrastructure. Colorado, for example, has many areas that will be getting recycling service for the first time. Maine also has many rural areas that previously had access to recycling but lost it in recent years. Meanwhile, in Maryland, collection service may be more common but local end markets are lacking for certain commodities. Jason Bergquist, vice president of consulting firm RecycleMe, said during the NERC event that he hears concerns from clients about where this is all headed. “If we get to a couple years down the road and we’ve got, let’s just pretend, 25 states with EPR, with different deadlines, different [covered material] lists, different definitions, different ecomodulation — my concern as a fan of EPR is that the pushback will be so significant that it could get existential for the producers,” he said, in terms of costs and compliance management. At the same time, Bergquist said the experiences of packaging EPR in Europe and Canada show it may take years to get toward any kind of harmonized system. Back at SPC Advance and the co-located How2Recycle Summit, California loomed large throughout the week when it came to these questions. Karen Kayfetz, chief of CalRecycle’s product stewardship branch, said regulators from different EPR states try to talk to one another as much as possible but in some cases they’re limited by the statutes that created these programs. “We each have our own legal frameworks we have to work within,” she said. “So harmonization starts with the legislatures, and that is not our responsibility, but it is something that we could see change and evolve over the coming years.” As all of these complex questions get worked out, Kayfetz reminded attendees that CalRecycle may currently be “the face” of the program but that’s not the long-term goal. “What would make me the happiest is if you leave here thinking ‘let’s go talk more to CAA.’ Because EPR is a policy mechanism that is meant to be a public-private partnership where the public entity ... is overseeing the PRO,” she said. “They are your partner and we are their police.” In a separate session, CAA’s Buckingham described the work of ramping up different state fee and reporting programs as building a plane while flying it. The group is working to streamline its own reporting processes as much as possible, but they and others anticipate things will only get more complicated in the near term. “2026 will bring with it a new set of EPR laws and recycled content laws,” predicted KDP’s Schwarze, “and they’re going to be different than what we have right now.” Read on Packaging Dive.
Press Releases

NERC’s Material Recovery Facilities (MRF) Commodity Values Survey Report for the period July - September 2025 showed a continued decline in the average commodity prices for Q3 2025. The average value of all commodities decreased by 21.90% without residuals to $75.14 and by 27.24% with residuals to $60.16, as compared to last quarter. Single stream decreased by 23.32% without residuals and 28.86% with residuals, while dual stream / source separated decreased by 17.33% without residuals and 21.76% with residuals compared to last quarter. Dual stream MRFs saw a slightly smaller decrease with residuals than single stream. Individual commodity price averages this quarter denote the decrease felt across all commodity categories apart from glass and the special case of bulky rigids.

The Northeast Recycling Council (NERC) published its Chemical Recycling Policy Position on May 30, 2025. The purpose of the policy statement is to articulate guiding principles for environmentally responsible chemical recycling of plastics. NERC supports the conservation of natural resources, waste minimization, and recognizes the role of recycling in reaching these goals. Plastic is a prevalent material for packaging and other products due to its material properties. Producing virgin plastic from fossil fuels is an extractive process with negative environmental and social impacts. Therefore, NERC supports reduction, reuse, and recycling processes that displace virgin production in plastics where environmentally preferable. You can view the policy statement here: https://www.nerc.org/chemical-recycling . The Policy Position was developed by the Subcommittee of the NERC Chemical Recycling Committee. Participants on the Subcommittee included Committee Chair Tom Metzner, Connecticut Department of Energy and Environmental Protection (CTDEEP); Claudine Ellyin, Massachusetts Department of Environmental Protection (MassDEP); John Fay, Northeast Waste Management Officials' Association (NEWMOA); Anthony Fontana, New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection (NJDEP), Retired ; Michael Fowler, New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection (NJDEP); Timothy Kerr, Maryland Department of the Environment (MDE), Left MDE ; Shannon McDonald, Maryland Department of the Environment (MDE); Chaz Miller, Ex-Officio, NERC Board; Elizabeth Moore, Connecticut Department of Energy and Environmental Protection (CTDEEP); Marc Moran, Pennsylvania Department Of Environmental Protection; Michael Nork, New Hampshire Department Of Environmental Services; Megan Schulz-Fontes, Northeast Recycling Council (NERC); and Richard Watson, Delaware Solid Waste Authority (DSWA). NERC created the Chemical Recycling Committee in 2022 with the goal of sharing information on new technologies called “chemical recycling.” The Committee shares information on the efficacy, cost, and impacts of these new technologies. Our Policy is the result of those efforts. The Committee is open to NERC state members and several advisory member organizations whose participation has been approved by the state members serving on the committee. NERC has published several other policy positions including the Post-Consumer Recycled Content Policy (2019) and Product Stewardship and Producer Responsibility Policy (2018), which can be found among others on NERC’s website: https://www.nerc.org/policy-positions-and-statements . For more information, contact Megan Schulz-Fontes, Executive Director, at megan@nerc.org .
Thought Leadership
2025 was not a good year for recycling markets. Prices went down for everything in your bin. The only real difference is how badly each material got hit and why. Let’s start with paper, the most important recyclable in terms of weight and volume. Old Corrugated Container (OCC, boxes) prices started rising in the spring of 2023, peaking for several months in the summer of 2024. A long slide then began and lasted for almost all of 2025. Prices for Residential Mixed Paper (RMP) did the same. Nationally, OCC is now at $46.88 per ton and RMP is $20.31 a ton. OCC went down by a third while RMP went down by half. The “good” news is that these prices have been lower in the last five years. RMP, after all, had a negative value early in 2020 and then for a few months in late 2022. (All prices in this article are national prices from RecyclingMarkets.net as of December 31). The 2023 rise and then fall of recycled paper prices was the result of increased capacity to use OCC and RMP as raw materials along with declining overall demand for boxes. New recycled content paper capacity started coming online in 2017, peaking in 2023 when five new mills opened. Those new mills, eager to build up supply lines, caused prices to go up. Existing capacity had no choice but to also pay more. At the same time, demand for new boxes was going down. In fact, box demand has been going down for four years. Something had to give. In 2025, nine existing paper mills announced they would be closing. Old, more expensive, and less efficient to operate, they couldn’t compete with the new mills. All four plastic resins lost value but the impact varied by resin. Natural HDPE, (mostly milk jugs) lost a third of its value. Polypropylene (mostly dairy products) went down by 40 percent. Color HDPE (consumer products such as detergent and shampoo) went down by 48 percent and PET beverage bottles went down by two thirds. Natural HDPE is 46.81 cents a pound. Even at the lower price, this resin remains in a good price range. PET and polypropylene are both 5.38 cents a pound. Recycled PET rose steadily from the summer of 2023 to the summer of 2024. Then it declined equally steadily until it reached a record low of 4.19 cents in early October of this year. Cheap recycled resin imports, too much domestic virgin PET resin and lower summer beverage demand gave prices nowhere to go but down. Recycled PET resin imports are now subject to tariffs, which may be responsible for its recent increase. Nonetheless, its price remains in the doldrums. Polypropylene generally has a low price except when new capacity is coming online and building up capacity. For 46 of the 72 months since January 2020, its price has been less than a dime a pound. For 17 months, it’s been at its current not very good price or less. Color HDPE is 2.81 cents a pound. This resin depends on construction markets because the color can’t be taken out of the resin. New housing starts have been in decline for four years. It also set a record low price in 2025. Aluminum and steel cans are recycling market’s happy place. Their prices went down by 9.3 and 8.7 percent. Aluminum cans have a national average price of 78.75 cents while steel cans go for $158.75 a ton. Over the last few years, the aluminum industry smartly expanded into non-alcoholic beverages such as water and fruit juices. Those new uses keep demand up. After sliding last year, steel can prices stabilized. As for glass, it’s price rarely changes. Clear glass bottles go for $38.56 a ton, brown for $27.19 and green for $10.31. Those prices all rose slightly in the spring of 2023. Mixed glass from single stream curbside collection has a “negative tipping fee” of $25.31 a ton. In other words, the MRF pays the end market to buy it. That price became slightly more negative this year. The glass industry has been in decline for some time, a victim of lighter weight aluminum cans and plastic bottles. In addition, Americans are drinking less alcohol. That’s the biggest user of glass bottles. Our beleaguered economy is hurting recycling markets. Recyclables are just raw materials looking for a buyer. Those buyers are purchasing managers making a bet on how much raw materials they will need for their companies’ products. This can be, say, aluminum cans, boxes to ship those empty cans to beverage companies or boxes to deliver filled cans to retail outlets. When buyers are optimistic, they buy more. In 2025, they were gloomy. Prices of all of these recyclables have been hurt by declining unit sales of consumer products and the resulting decline in box demand. We are in a “ K-shaped” economic recovery from the pandemic. This means the recovery’s impact varied by economic status. Wealthy households now account for half of consumer spending on goods and services. They spend more on “services” such as trips and entertainment than on goods. Lower income households, however, are squeezed between paying for necessities such as housing, health care, insurance and food before everything else. They are pinching their nickels and looking for bargains. Simply stated, due to the K-shaped recovery, sales are down and we need fewer packages and shipping boxes. So what will happen in 2026? The loss of so much older paper capacity is bringing demand and supply back into a better balance. Look for prices to rebound a bit. Plastic prices will remain soft barring a reversal of the K-shaped recovery. PET prices, have the most potential if beverage demand returns. Color HDPE, will remain in the doldrums until new housing construction increases. Natural HDPE will stay where it is or go up a bit. Polypropylene will probably stay where it is. As for glass, change isn’t likely. I realize that’s not optimistic. Given the projected rise in health, insurance and energy costs this year, Americans will still be pinching pennies. Box production will decline as unit sales fall. Our K-shaped economy needs to become a rising economic tide lifting all boats. Recyclables, afterall, are commodities subject to the economy’s ups and downs. When our economy truly rebounds, recycling markets will thrive again. Read on Waste360.

Recycling coordinators know that some people and locations are stubbornly indifferent to recycling. COVID has ruptured civic values and behavior. Creating a recycling culture is harder than ever. Producers know how to sell their products. Now they need to learn how to sell recycling. On July 1, Oregon’s packaging and paper extended producer responsibility (EPR) program begins operating. This will be a first in our country. “Producers”, instead of local governments or private citizens, will be paying to recycle packages and paper products. Colorado’s program begins operating early in 2026. For years we have heard the theory of how packaging EPR will work. At last, we will get results. Five other states also have laws. Their programs should all be operating by 2030. None of the state laws have identical requirements. The Circular Action Alliance, the “producer responsibility organization” responsible for managing the program in most of those states, knows it has a lot on its plate. EPR laws are not new to the U.S. Thirty-two states already have laws that cover a wide variety of products such as electronics, paint, mattresses, batteries, etc. Those laws are relatively simple. Most cover one product. The producer group is a small number of companies. Goals and programs are focused and narrow. They are a mixed bag of success and failure. Packaging EPR is far more complex. The number of covered products is way higher. Thousands of companies are paying for these programs. Goals are challenging. Some are impossible to meet. In addition, local governments treat recycling as a normal service. Their residents will still call them if their recyclables aren’t picked up. It probably hasn’t helped that advocates tout EPR as the solution for recycling’s problems. We are told we will have more collection and better processing with higher recycling rates. Markets will improve and even stabilize. Some of this will happen, but not all. Collection and processing should go smoothly in Oregon. The state has high expectations for recycling. I have no doubt recycling will increase. Collection programs will blanket the state, giving more households the opportunity to recycle. I’m not sure, though, how much of an increase we will see. Recycling coordinators know that some people and locations are stubbornly indifferent to recycling. COVID has ruptured civic values and behavior. Creating a recycling culture is harder than ever. Producers know how to sell their products. Now they need to learn how to sell recycling. Another challenge is the “responsible end market” requirements. You’ve probably seen pictures of overseas dumps created by unscrupulous or just naïve plastics “recyclers”. In response, Oregon and the other states are requiring sellers and end markets to prove they are “responsible”. They must provide information about who and where they are, how they operate, how much was actually recycled, and more. Recycling end markets pushed back. Paper and metals recyclers argue they shouldn’t be covered. They don’t cause those problems. As for plastics, the general manager of one of America’s largest plastics recycling companies said his company now spends time and money gathering data and filling out forms to prove they’re “responsible”. His virgin resin competitors don’t have to. Ironically, we now import more plastics for recycling than we export. Maybe those countries should impose similar requirements on their plastics recyclers. Colorado faces unique problems. The mountain state is large. Its population is concentrated on the I-25 corridor running north and south through Denver with low population density elsewhere. Recycling collection and processing is limited as are end markets. To make matters worse, slightly more than half of its households use “subscription” services for waste and recycling collection. Those services are funded by the households, not by taxpayers. EPR doesn’t have this experience in other countries. Colorado gets to blaze this trail. The second state to go live poses substantive challenges for producers. The good news for both states? Local governments that pay for recycling collection and processing will see most of those costs go away. Consumers are unlikely to see prices rise, for now. National companies will simply spread their costs among all 50 states. Local and regional producers, unfortunately, don’t have that advantage. As for improved markets, remember that recyclables are and always will be commodities subject to the ups and downs of the economy. I don’t see substantive changes in recycling markets unless the producer group’s members try to manipulate markets to their own advantage. 2025 saw new laws and changes to existing laws. Maryland and Washington became the sixth and seventh packaging EPR states. At the same time, California is rewriting its regulations and Maine significantly revised its law. Some of these changes narrowed EPR’s scope to the dismay of advocates. I’m a member of Maryland’s EPR Advisory Council. We’ve been meeting for a year, discussing the Needs Assessment and now our new law. We have our own unique set of challenges. We also have a big advantage. We can learn from Oregon’s and Colorado’s experiences. Tune in next year to learn how we are progressing. Read on Waste360.
Member Spotlights

Established in 2015, Apparel Impact has been working within their community to reduce textile waste, fight clothing insecurity, create jobs, and ensure those in the community in need of clothing never go without. This family and veteran owned company is built on the foundation of disruption for good. The Apparel Impact team has been working to make real changes in an industry that has remained the same for many decades. They continuously push for transparency, accountability, and working solutions in the field. Today Apparel Impact works with over 1,800 partners and locations, including schools, towns, nonprofits, national brands, and small businesses across six states. Apparel Impact is also working to bring textile sorting and grading capacity back to the Northeast, while launching upcycling brands aimed at scaling textile reuse across the region. For Apparel Impact, it is all about “changing the way people think about clothing, proving a for-profit company can still put people and communities first, and making sure what we collect helps someone’s life, not a landfill.” Their impact and reach continue to grow every year. “Textile recovery only works at scale. It takes leadership, accountability, and real collaboration across states and sectors. We joined NERC because we believe in building infrastructure that actually changes outcomes, not just talking about it. We’re proud to stand with the NERC and others in the Northeast who are ready to move the industry forward.” NERC is excited to welcome Apparel Impact to our growing group of textile focused members. We look forward to amplifying their voice and helping to expand textile recovery in any way we can. For more information on Apparel Impact visit.

For more than a decade, Sensoneo has been driving innovation across the waste and recycling industry worldwide. Headquartered in Europe and active in more than 80 countries, the company has recently expanded into the United States by opening its Boston office. From the outset, its mission has been clear: to help cities, businesses, and governments address two of the sector’s most pressing challenges—operational efficiency and data transparency. Sensoneo brings proven, large-scale experience, operating nationwide end-to-end IT platforms for deposit return systems (bottle bill programs) in nine countries and supporting Extended Producer Responsibility programs with robust data management, reporting, and compliance tools. Its smart waste solutions power the world’s largest deployment of sensor-based waste-monitoring technology, enabling municipalities and facilities to optimize collection operations. “With the launch of our U.S. subsidiary, we are excited to expand collaboration with organizations advancing sustainable materials management and stronger recycling systems,” said Martin Nestepny, CEO of Sensoneo USA. “As a global technology partner, Sensoneo supports PROs, recyclers, and policymakers with actionable data to enhance program performance, ensure regulatory compliance, and deliver measurable environmental outcomes - priorities that closely align with NERC’s mission.” NERC is pleased to welcome Sensoneo to its growing membership and looks forward to supporting the company’s work to improve performance and drive greater effectiveness across the waste and recycling industry. For more information on Sensoneo visit.

Planet Aid is a nonprofit established in 1997 to divert clothes and shoes from the U.S. waste stream and fundraise for community development programs around the world. With thousands of donation bins and centers across the Northeast, Mid-Atlantic and Midwest, Planet Aid’s mission is to inspire positive change by making it easy for donors, partners and communities to take small steps that add up to a big impact. Over three decades, Planet Aid has collected more than two billion pounds of clothes and shoes for reuse. These donations have helped Planet Aid raise more than $100 million to fund community-led projects in the U.S., Africa, Asia, and Latin America. With headquarters just outside Baltimore, MD, Planet Aid serves thousands of communities in 14 states, including New York, New Jersey, Maine, Massachusetts, Connecticut and more. For those without a yellow collection bin or white donation center nearby, they've developed a donation through mail option. By partnering with Give Back Box, you can pack up and mail your donation items directly to their thrift store. This inclusive approach allows them to reach more communities, diverting even more waste that may have gone to a landfill or incinerator. “Planet Aid is excited to join NERC, an organization that shares our goals of minimizing waste, conserving natural resources, and advancing a sustainable economy,” said Uli Stosch, Planet Aid’s Chief Officer of Strategic Development. “We looking forward to collaborating with NERC’s members to help U.S. communities in the Northeast minimize textile waste while maximizing reuse to limit the negative impacts of fast fashion.” NERC is excited to welcome Planet Aid into our growing group of nonprofit members. We look forward to helping share the excellent work they are doing in the NE and around the world. For more information on Planet Aid visit.




